400-621-6806
周一至周六
8:00-18:00

服务电话:400-621-6806
地址:天津市武清区国际企业社区A5号楼五层,301700
邮箱:
| 产品编号 | KMP2236 |
|---|---|
| 产品名称 | Human Biotinylated CD28 Protein, Fc Tag, Avi Tag |
| 产品描述 | The Human Biotinylated CD28 Protein(KMP2236) is produced in HEK293 Cells and the target gene encoding Asn19-Pro152 is expressed with a Fc, Avi tag at the C-terminus. |
| 物种 | Human |
| 宿主 | HEK293 Cells |
| 规格 | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| 纯化方式 | Affinity purification |
| 内毒素水平 | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| 缓冲体系 | 20mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0 |
| SDS-PAGE | 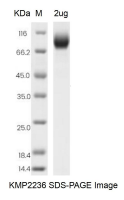 |
| 功能 | Involved in T-cell activation, the induction of cell proliferation and cytokine production and promotion of T-cell survival. Enhances the production of IL4 and IL10 in T-cells in conjunction with TCR/CD3 ligation and CD40L costimulation (PubMed:8617933). Isoform 3 enhances CD40L-mediated activation of NF-kappa-B and kinases MAPK8 and PAK2 in T-cells (PubMed:15067037). |
| 产品背景 | T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein CD28(CD28) is a single-pass typeI membrane protein which contains one Ig-likeV-type(immunoglobulin-like) domain. It belongs to the immunoglobulin(Ig) superfamily. CD28 is one of the molecules expressed on T cells that provide co-stimulatory signals, which are required for T cell activation. CD28 co-stimulation is necessary for CD4 positive T-cell proliferation and survival, interleukin-2 production, and T-helper type-2 development. Human post-thymic regulatory T cells require CD28 co-stimulation to expand and maintain potent suppressive function in vivo. Apoptosis plays a key role in the age-related decline of CD28 expression and in immunosenescence. CD28 is the receptor for CD80(B7.1) and CD86(B7.2). When activated by Toll-like receptor ligands, the CD80 expression is upregulated in antigen presenting cells(APCs). The CD86 expression on antigen presenting cells is constitutive. CD28 is the only B7 receptor constitutively expressed on naive T cells. |
| 保存条件 | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| 说明 | This product is for research use only. |
| 参考文献 | 1.J. Exp. Med. 199:1025-1031 (2004) 2.J. Immunol. 156:3133-3140 |